How to evaluate the sustainability of electronic products

How to Evaluate the Sustainability of Electronic Products
As we navigate the digital age, electronic devices have become an integral part of our daily lives. However, the rapid pace of technological advancements has led to a significant increase in electronic waste (e-waste), posing substantial environmental challenges. For middle-aged individuals aged 40-55 in the United States, making informed choices about sustainable electronics can seem daunting, but it’s crucial for reducing our ecological footprint. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you evaluate the sustainability of electronic products.

Understanding Sustainability in Electronics
Sustainability in electronics encompasses several key areas: environmental impact, social responsibility, and economic viability. It involves ensuring that products are designed, manufactured, and disposed of in ways that minimize harm to the environment, promote fair labor practices, and contribute positively to the economy.

Challenges in Sustainable Electronics
-
Complex Supply Chains: The electronics supply chain is global and complex, involving raw material extraction, manufacturing, and transportation. Ensuring transparency and ethical practices throughout this chain is challenging .1.
-
Material Sourcing: Securing responsibly sourced materials is difficult due to the environmental impact of mining and extraction. Finding alternatives with lower ecological footprints while maintaining performance is a significant challenge .1.
-
Energy Consumption: The production and use of electronics are energy-intensive. Reducing carbon footprints requires innovative solutions and a commitment to renewable energy .1.
-
Battery Issues: Batteries require raw materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, often mined under questionable conditions. Proper disposal is crucial to prevent toxic leaks .1.
-
E-Waste: Rapid technological advancements lead to frequent device obsolescence, resulting in a growing e-waste problem. Proper recycling and end-of-life management are essential .1.

Strategies for Sustainable Electronics

1. Responsible Sourcing of Raw Materials
Manufacturers should prioritize materials with lower ecological footprints and ensure compliance with regulations like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances). This includes avoiding conflict minerals and promoting fair labor practices .1.

2. Sustainable Design Practices
Designing products for longevity, modularity, and recyclability is crucial. This includes incorporating energy-efficient innovations and educating consumers on responsible device use .1.

3. Green Production Processes
Adopting energy-efficient manufacturing processes, reducing material waste, and using renewable energy sources are key strategies. Techniques like Material Flow Cost Accounting help identify and reduce material costs .1.
4. Recycling and End-of-Life Management
Implementing take-back programs, tech refurbishment, and closed-loop recycling systems ensures that valuable materials are recovered and reused, reducing e-waste .1.

Evaluating Sustainability in Electronic Products
When evaluating the sustainability of electronic products, consider the following factors:
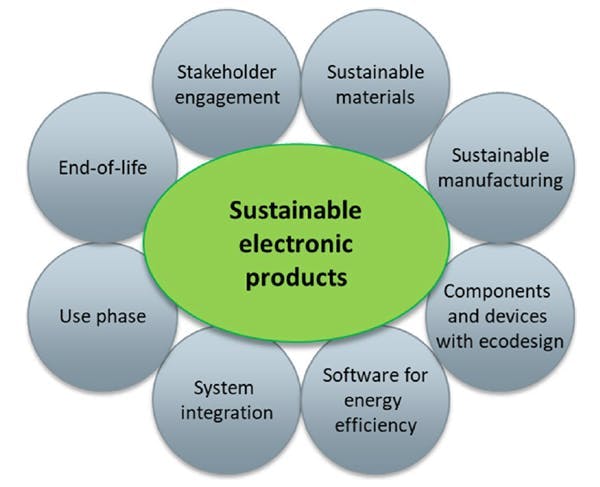
1. Material Composition
-
Recycled Materials: Look for products made with recycled materials, such as recycled plastics or metals.
-
Biodegradable Materials: Some products use biodegradable materials like plant-based biopolymers.

2. Energy Efficiency
-
Low Power Modes: Devices with low power modes or energy-saving features reduce energy consumption.
-
Renewable Energy Compatibility: Products compatible with renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, are more sustainable.
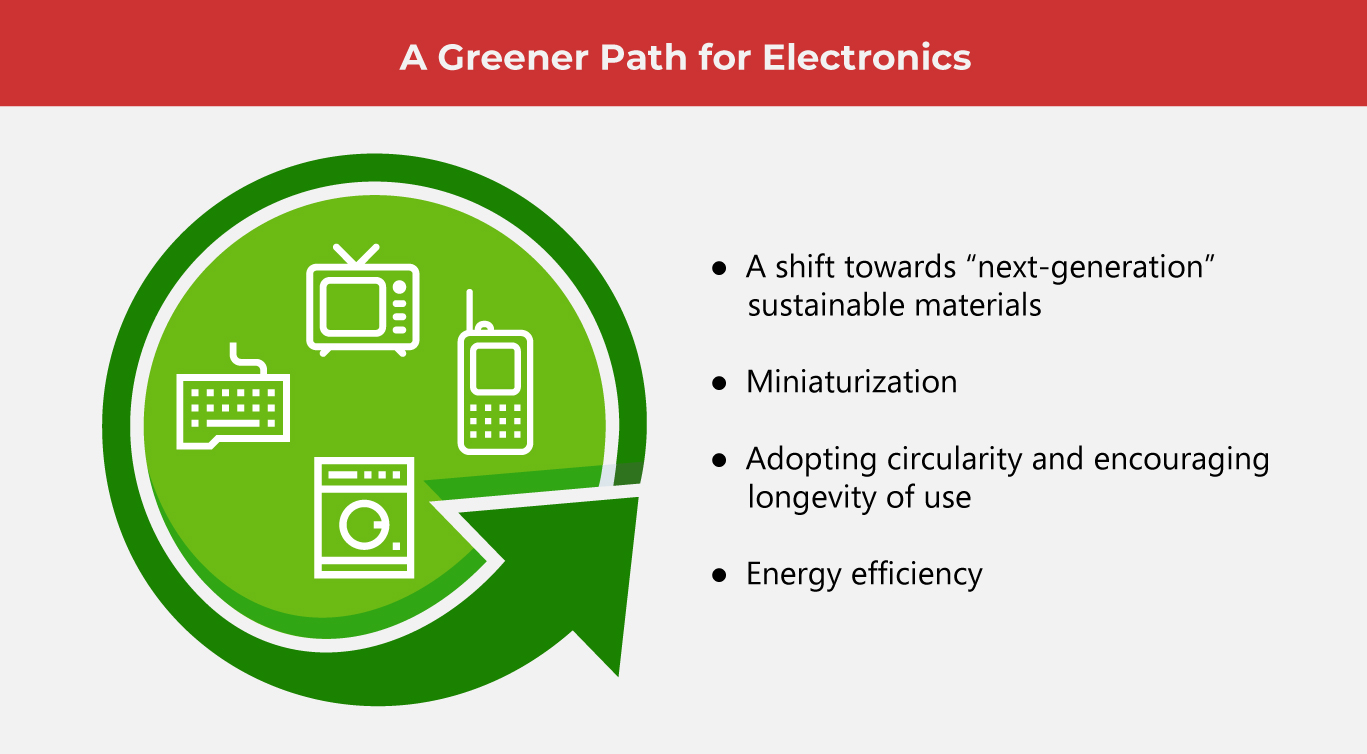
3. Design for Longevity
-
Modular Design: Products designed with modular components can be easily repaired or upgraded, extending their lifespan.
-
Durability: Durable products reduce the need for frequent replacements.
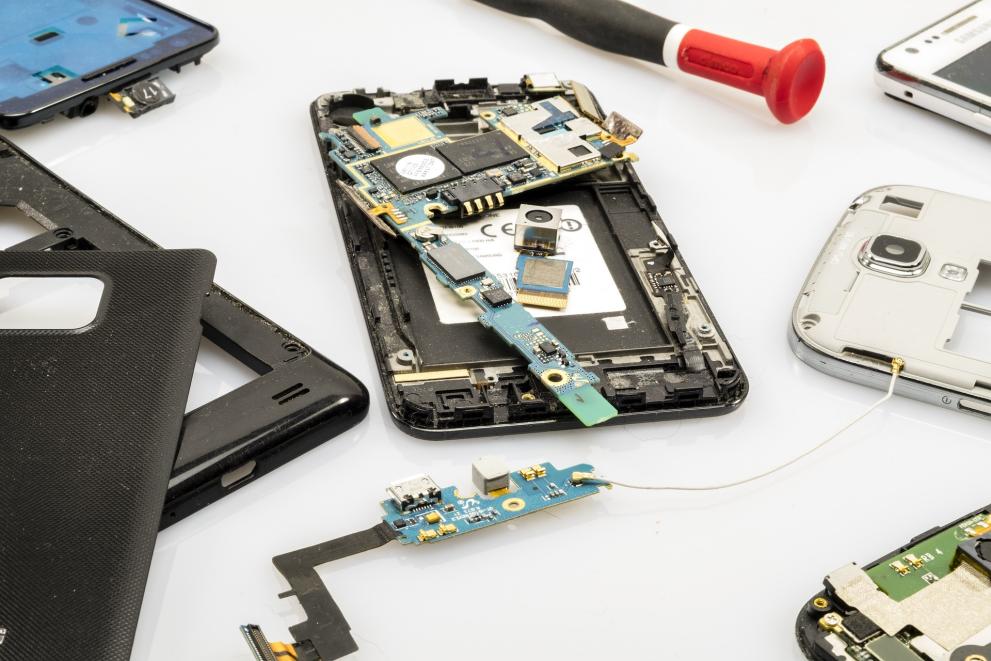

4. Recyclability
-
Easy Disassembly: Products designed for easy disassembly facilitate recycling.
-
Recycling Programs: Manufacturers offering take-back or recycling programs for their products contribute to sustainable end-of-life management.

5. Supply Chain Transparency
-
Independent Verification: Look for products certified by independent organizations that verify sustainability claims.
-
Supply Chain Audits: Companies that conduct regular audits to ensure ethical practices in their supply chains are more sustainable.

6. Social Responsibility
-
Fair Labor Practices: Ensure that the manufacturer adheres to fair labor standards and treats workers ethically.
-
Community Engagement: Companies involved in community initiatives and social responsibility projects demonstrate a broader commitment to sustainability.

Practical Tips for Consumers
-
Research Brands: Look for brands known for their sustainable practices, such as Fairphone, Apple, and Samsung .6 .9.
-
Check Certifications: Verify if products are certified by organizations like TCO Development or the Carbon Trust .3 .5.
-
Read Reviews: Pay attention to reviews from other consumers and environmental groups to get a comprehensive view of a product’s sustainability.
-
Consider Refurbished Options: Buying refurbished electronics reduces e-waste and supports a circular economy .10.
-
Participate in Recycling Programs: Engage with manufacturers’ recycling initiatives to ensure responsible end-of-life management of your devices .1.

Emerging Trends in Sustainable Electronics
-
Eco-Friendly Accessories: Brands like Nimble and Anker offer eco-friendly accessories made from recycled materials .5 .9.
-
Solar-Powered Devices: Solar-powered chargers and devices are becoming increasingly popular for their ability to reduce reliance on conventional electricity .7.
-
Biodegradable Materials: The use of biodegradable materials in phone cases and other accessories is on the rise .7.

Conclusion
Evaluating the sustainability of electronic products requires a holistic approach, considering environmental impact, social responsibility, and economic viability. By choosing sustainable electronics, consumers can contribute to reducing e-waste, conserving resources, and promoting eco-friendly practices. As technology continues to evolve, embracing sustainability will become increasingly important for both individuals and businesses. By making informed choices and supporting sustainable brands, we can pave the way for a greener future.

Additional Resources
For those interested in diving deeper into sustainable electronics, here are some additional resources:








