Early Warning Signs of Type 2 Diabetes

Early Warning Signs of Type 2 Diabetes: A Guide for Middle-Aged Individuals
As we age, our bodies undergo various changes that can increase the risk of developing health conditions like type 2 diabetes. This condition is particularly prevalent among middle-aged individuals, often due to lifestyle factors and genetic predispositions. Recognizing the early warning signs of type 2 diabetes is crucial for timely intervention and management. In this article, we will explore these signs, discuss risk factors, and provide practical tips for prevention and management tailored to the needs of middle-aged individuals in the United States.
Introduction to Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by the body’s inability to effectively use insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels. Over time, this can lead to high blood sugar levels, which may cause serious health complications if left untreated. The onset of type 2 diabetes can be gradual, and symptoms may be mild or even absent in the early stages, making early detection challenging.
Early Warning Signs of Type 2 Diabetes
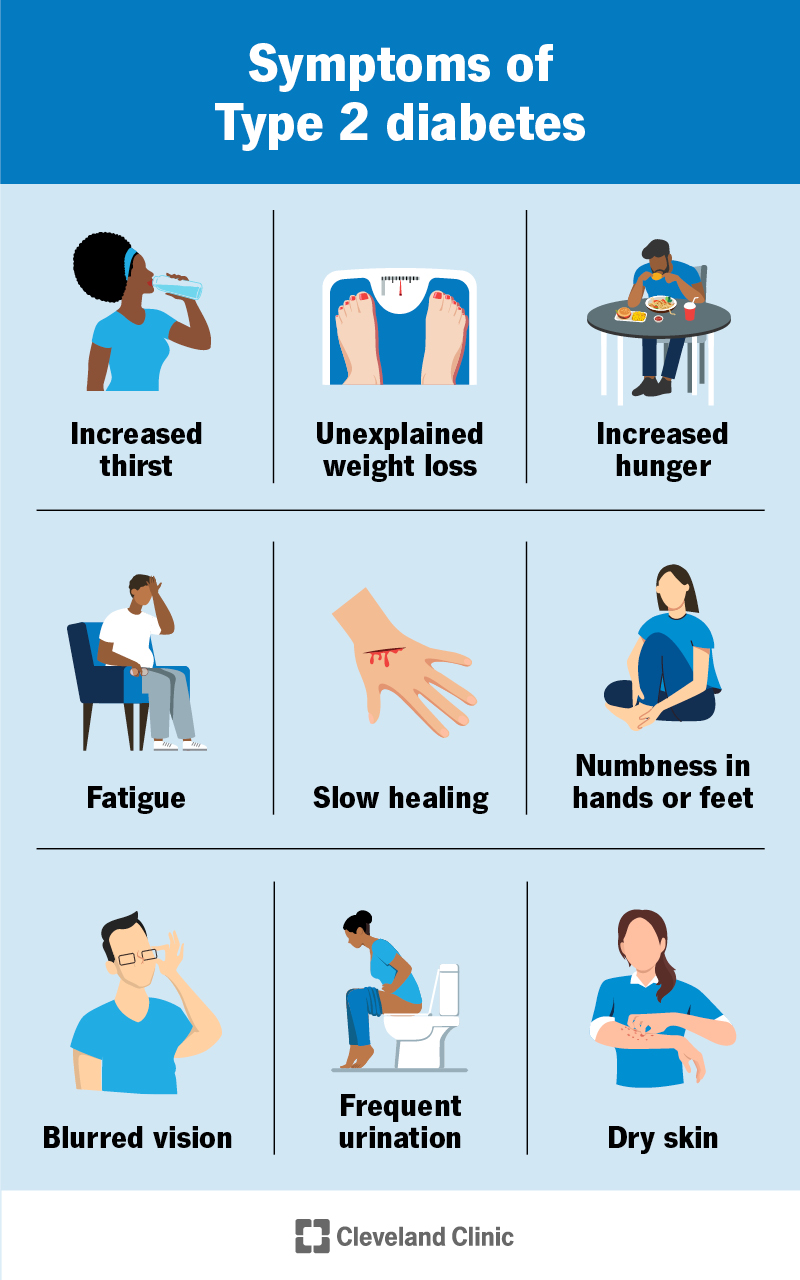
While type 2 diabetes can develop without noticeable symptoms, there are several early warning signs that you should be aware of:
-
Increased Thirst and Frequent Urination: High blood sugar levels cause your kidneys to work harder to filter and remove excess glucose from your blood. This process results in more urine production, leading to frequent trips to the bathroom and increased thirst as your body tries to replenish lost fluids .10 .13.
-
Fatigue and Tiredness: When your body cannot effectively use insulin, glucose cannot enter your cells to provide energy. This can leave you feeling tired and weak, even after resting .10 .13.
-
Increased Hunger: Since glucose is not entering your cells, your body may signal that it needs more energy, leading to increased hunger .10 .13.
-
Blurred Vision: High blood sugar levels can cause the lenses in your eyes to swell, affecting your ability to focus .10 .13.
-
Slow Healing of Cuts and Wounds: High blood sugar levels can impair your body’s ability to heal wounds efficiently .2 .10.
-
Tingling or Numbness in Hands and Feet: This is often a sign of nerve damage due to prolonged high blood sugar levels .2 .10.
-
Recurrent Infections: High blood sugar levels can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections .2 .10.
-
Unintentional Weight Loss: Despite eating more, you might lose weight because your body is using muscle and fat for energy instead of glucose .10 .13.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/diabetes-signs-and-symptoms-5104883_Final-2f62c1beeb864b4b891c5f0c6c1d9419.jpg)
Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
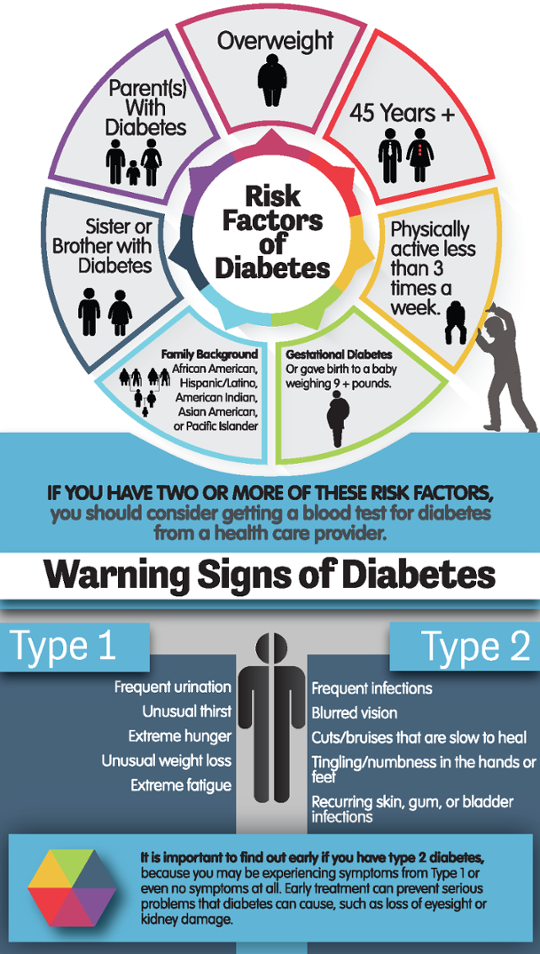
Understanding your risk factors can help you take proactive steps to prevent or manage type 2 diabetes:
-
Age: The risk increases with age, especially after 35 .3.
-
Family History: Having a family history of diabetes increases your risk .3.
-
Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Hispanics/Latinos, and American Indians, are at higher risk .3.
-
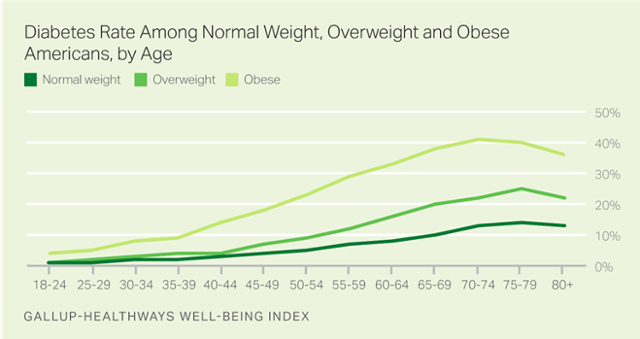
Obesity: Being overweight or obese is a significant risk factor .3 .11.
-
Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can increase your risk .3.
-
Prediabetes: If you have prediabetes, you are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes .3.
Prevention and Management Strategies
While some risk factors cannot be changed, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes or help manage the condition if you already have it:

1. Stay Active
Regular exercise not only helps control blood sugar levels but also improves overall health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening exercises twice a week .5 .6. Activities like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming are excellent choices.

2. Choose Healthy Foods
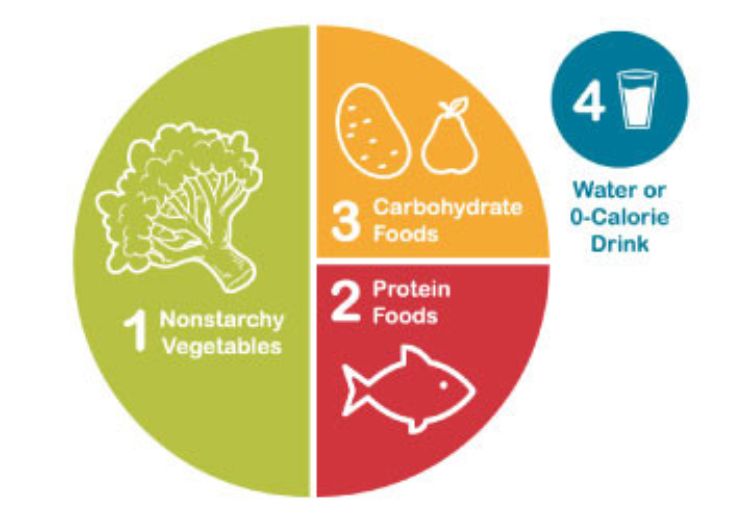
Focus on a balanced diet rich in non-starchy vegetables, lean proteins, and complex carbohydrates. The “diabetes plate method” is a helpful guide: fill half your plate with vegetables, one-quarter with lean protein, and the remaining quarter with complex carbohydrates .5.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
If you are overweight, losing weight can help prevent or manage type 2 diabetes. Consult with a healthcare provider to create a safe weight loss plan .