Essential Vaccination Schedule for People Over 50

Essential Vaccination Schedule for People Over 50
As we age, our immune systems naturally weaken, making us more susceptible to serious infections. For individuals over 50, vaccinations are crucial for maintaining health and preventing complications from diseases. This article will guide you through the essential vaccines recommended for people in this age group, highlighting their importance, benefits, and practical tips for staying up-to-date.

Introduction to Vaccinations for Adults Over 50
Vaccinations are not just for children; they play a vital role in protecting adults from infectious diseases. As people age, their immune systems become less effective at fighting off infections, which can lead to severe health complications. Vaccines help bridge this gap by providing immunity against diseases that are more common or severe in older adults.

Essential Vaccines for Adults Over 50

1. Annual Influenza Vaccine
The flu vaccine is recommended for everyone aged six months and older, but it’s particularly important for individuals over 50, especially those with chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease. The flu can lead to serious complications such as pneumonia, which is more dangerous in older adults. There are different types of flu vaccines available, including the Fluzone High-Dose vaccine, which is specifically designed for seniors and offers additional protection .2 .10.

2. Pneumococcal Vaccines
Pneumococcal vaccines protect against pneumonia and other serious infections caused by pneumococcal bacteria. The CDC has recently lowered the age recommendation for pneumococcal vaccination from 65 to 50 years old, emphasizing its importance for this age group .1. There are two main types of pneumococcal vaccines: pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs) like Prevnar 20 and pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccines (PPSVs) like Pneumovax 23 .2 .10.

3. Shingles Vaccine (Shingrix)
Shingles is caused by the reactivation of the chickenpox virus and can lead to severe pain and complications. The CDC recommends that all healthy adults aged 50 and older receive two doses of Shingrix, spaced two to six months apart. Shingrix is more effective than the older Zostavax vaccine and is recommended even if you’ve had Zostavax or can’t remember if you’ve had chickenpox .10.

4. COVID-19 Vaccines
COVID-19 vaccines are crucial for all adults, especially those over 50. The CDC recommends that adults aged 65 and older receive a second dose of the COVID-19 vaccine for the current season. Additionally, individuals aged six months to 64 who are moderately or severely immunocompromised may need additional doses under shared clinical decision-making .1.
5. Tdap/Td Vaccines
These vaccines protect against tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis (whooping cough). Adults should receive a Tdap booster once in place of one of their Td boosters, which are recommended every ten years .13.

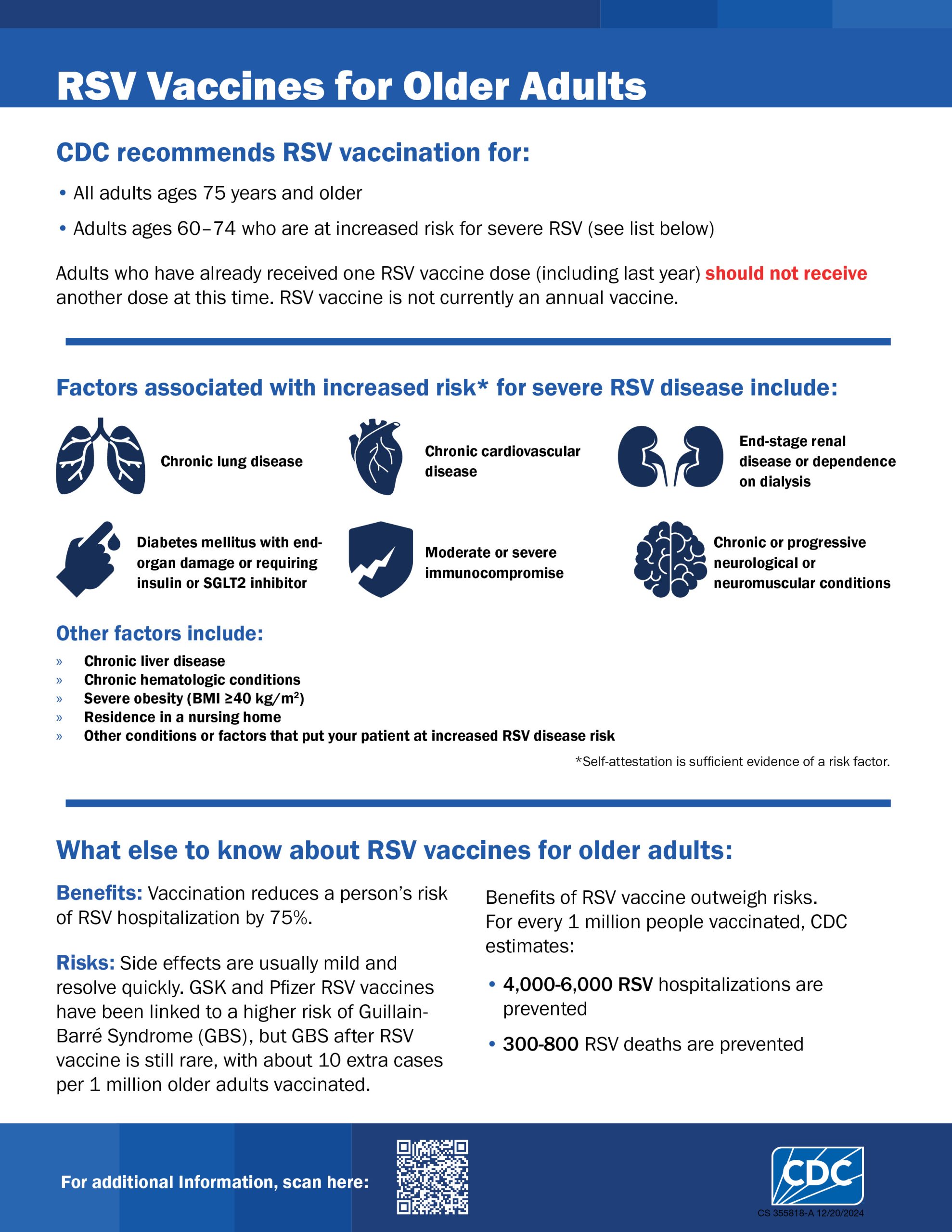
6. RSV Vaccine (for those aged 75 and older)
For individuals aged 75 and older, the RSV vaccine is recommended to protect against respiratory syncytial virus, which can cause severe respiratory infections in older adults .13.
Benefits of Vaccinations for Adults Over 50
Vaccinations offer numerous benefits for older adults:
-
Protection Against Serious Diseases: Vaccines prevent infections that can lead to severe complications, such as pneumonia, meningitis, and sepsis.
-
Reduced Hospitalization and Mortality: Studies have shown that vaccinations like the flu vaccine can significantly reduce hospitalizations and deaths among older adults .3.
-
Improved Quality of Life: By preventing diseases, vaccinations help older adults maintain their independence and quality of life.
-
Reduced Healthcare Costs: Vaccinations can reduce the need for costly medical interventions and hospital stays.

Practical Tips for Staying Up-to-Date

1. Consult Your Healthcare Provider
Discuss your vaccination needs with your doctor or pharmacist. They can help determine which vaccines are appropriate based on your health status and age.

2. Keep Track of Vaccinations
Maintain a record of your vaccinations. This can be done through your healthcare provider or by keeping a personal log.
3. Check Insurance Coverage
Most recommended vaccines are covered by insurance, including Medicare. Check with your insurance provider to understand what is covered.

4. Address Barriers to Vaccination
Common barriers include lack of awareness, cost concerns, and transportation issues. Discuss these with your healthcare provider, and explore resources like free or low-cost vaccines if needed .7 .8.

Overcoming Common Misconceptions
Some individuals may have misconceptions about vaccines, such as concerns about side effects or effectiveness. It’s important to address these concerns with healthcare providers, as they can provide accurate information and reassurance.

Conclusion
Vaccinations are a vital part of maintaining health and preventing serious diseases in adults over 50. By staying informed about recommended vaccines and addressing any barriers to vaccination, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their health and well-being. Remember, vaccinations are not just a personal choice; they contribute to community health by reducing the spread of infectious diseases.

Additional Resources
For more information on vaccinations and to find resources near you:
-
CDC Website: Visit the CDC’s website for the latest vaccine schedules and recommendations.
-
Local Health Departments: Contact your local health department for information on vaccine availability and access.
-
Healthcare Providers: Consult with your doctor or pharmacist for personalized advice on vaccinations.
By prioritizing vaccinations, you can enjoy a healthier life as you age. Stay informed, stay protected.








