The Effects of Vitamin D and How to Supplement Safely

The Effects of Vitamin D and How to Supplement Safely
Vitamin D is often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin” due to its production in the skin upon exposure to sunlight. However, its importance extends far beyond just bone health, playing a crucial role in cardiovascular health, immune function, and even mental well-being. For middle-aged individuals, maintaining adequate vitamin D levels is essential to prevent deficiencies that can lead to various health issues. This article will explore the effects of vitamin D, its benefits, and how to supplement safely, tailored specifically for individuals aged 40-55 in the United States.
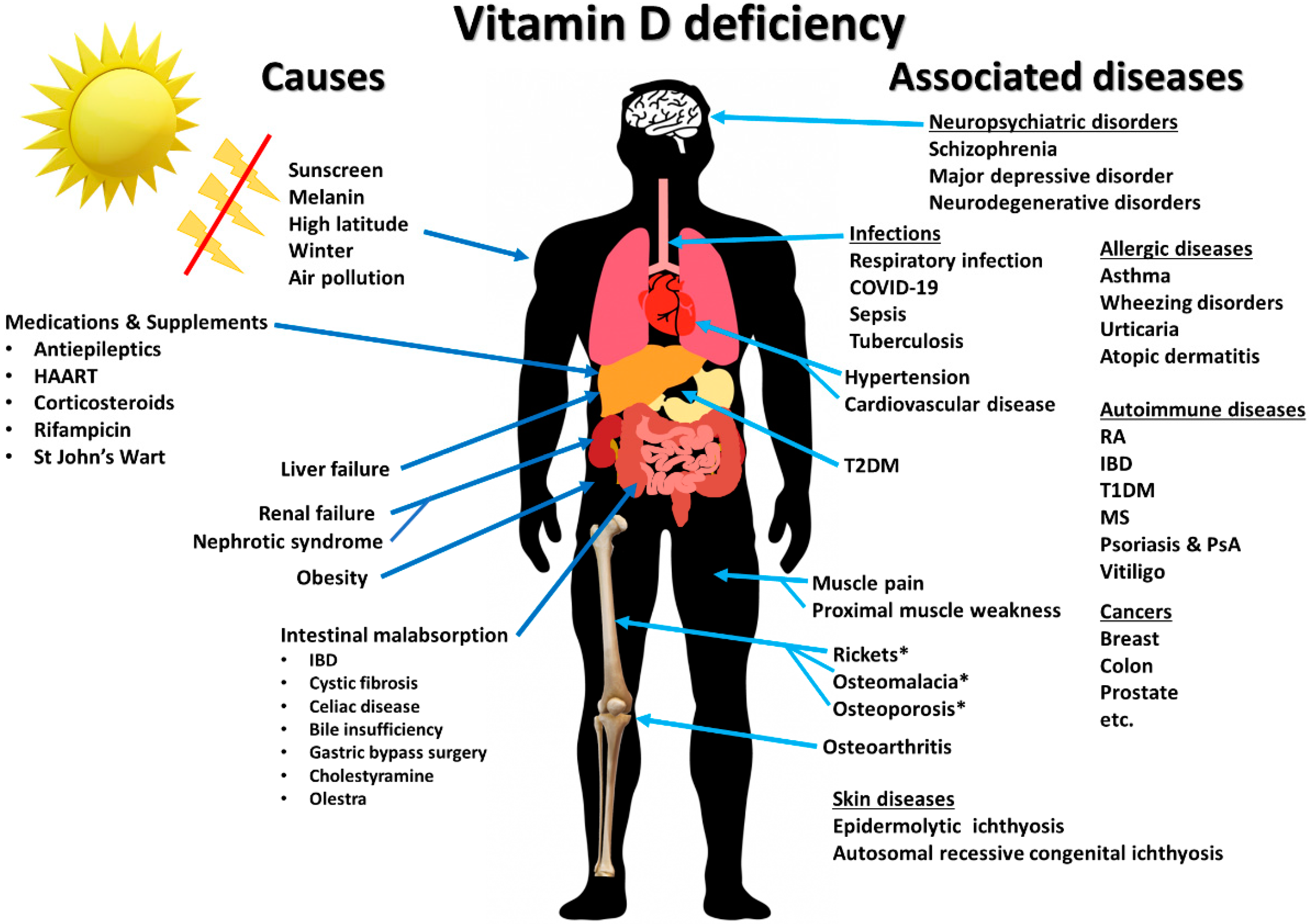
Understanding Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is crucial for calcium absorption and bone health. It also has roles in immune function, inflammation reduction, and possibly in the prevention of diseases like diabetes and certain cancers. There are two main forms of vitamin D: D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol), with D3 being more effective at raising blood levels of vitamin D.
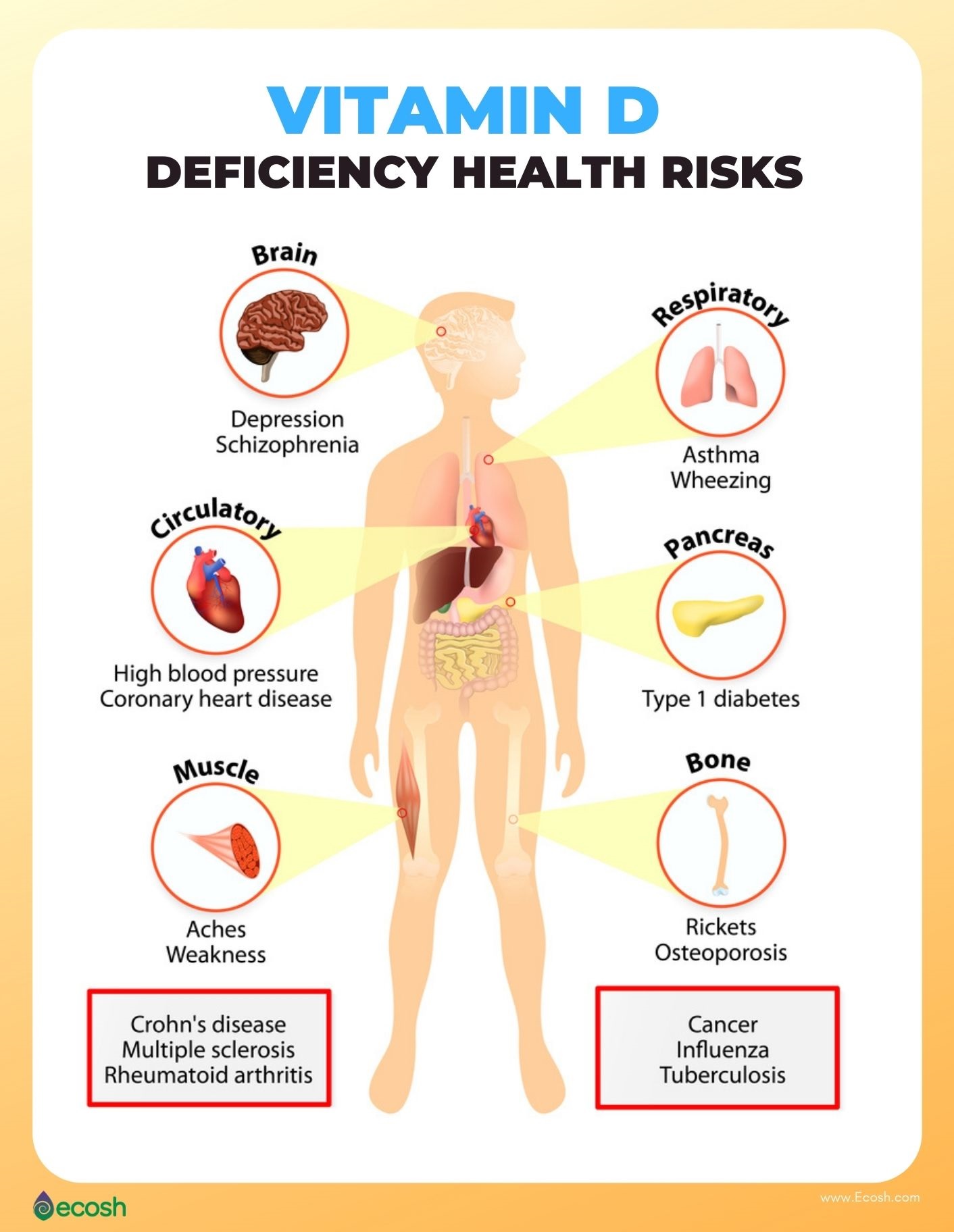
Sources of Vitamin D
-
Sunlight: The primary source of vitamin D is sunlight. However, factors like age, skin tone, and geographical location can affect how much vitamin D is produced from sun exposure.
-
Diet: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are natural sources. Fortified foods such as milk, yogurt, and cereals also provide vitamin D.
-
Supplements: Available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and chewable gummies.

The Importance of Vitamin D for Middle-Aged Individuals
As people age, their ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight decreases, making supplementation more necessary. Vitamin D deficiency is linked to several health issues:
-
Bone Health: Essential for maintaining strong bones and preventing conditions like osteoporosis.
-
Cardiovascular Health: Low levels of vitamin D have been associated with increased cardiovascular risk, including hypertension and heart disease .1.
-
Immune Function: Plays a role in immune system regulation, potentially reducing the risk of infections.
-
Mental Health: Some studies suggest a link between vitamin D deficiency and depression.

How to Supplement Vitamin D Safely

Recommended Dosage
For adults aged 40-55, the recommended daily intake of vitamin D is generally 600 IU (International Units), though some experts suggest higher doses may be beneficial for maintaining optimal levels, especially if you have limited sun exposure or are at risk of deficiency .8 .10.
-
General Recommendation: 600-800 IU per day.
-
Higher Risk Groups: Consider consulting a healthcare provider for personalized advice if you have darker skin, are obese, or have limited sun exposure.

Choosing the Right Supplement
-
Vitamin D3 vs. D2: D3 is generally preferred as it is more effective at raising blood levels.
-
Form: Capsules, tablets, or chewable gummies are available. Choose a form that suits your needs.
-
Combination Supplements: Some supplements combine vitamin D with calcium for enhanced bone health.

Safety Considerations
-
Upper Limit: The safe upper limit for vitamin D intake is 4,000 IU per day for most adults .5 .12.
-
Blood Tests: If you’re considering supplementation, it’s advisable to have your vitamin D levels checked to determine the appropriate dosage.
Lifestyle Changes to Boost Vitamin D
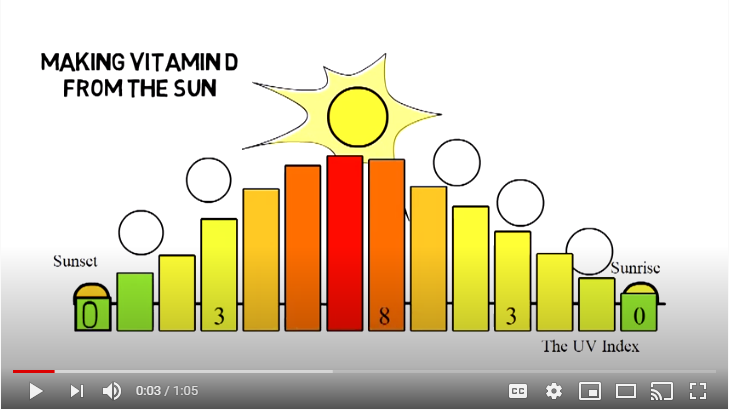
Increase Sun Exposure
-
Spend time outdoors, especially during peak sun hours (10 AM to 4 PM), but always use sunscreen to protect against skin damage.
-
Aim for 10-15 minutes of midday sun exposure on arms and legs several times a week.
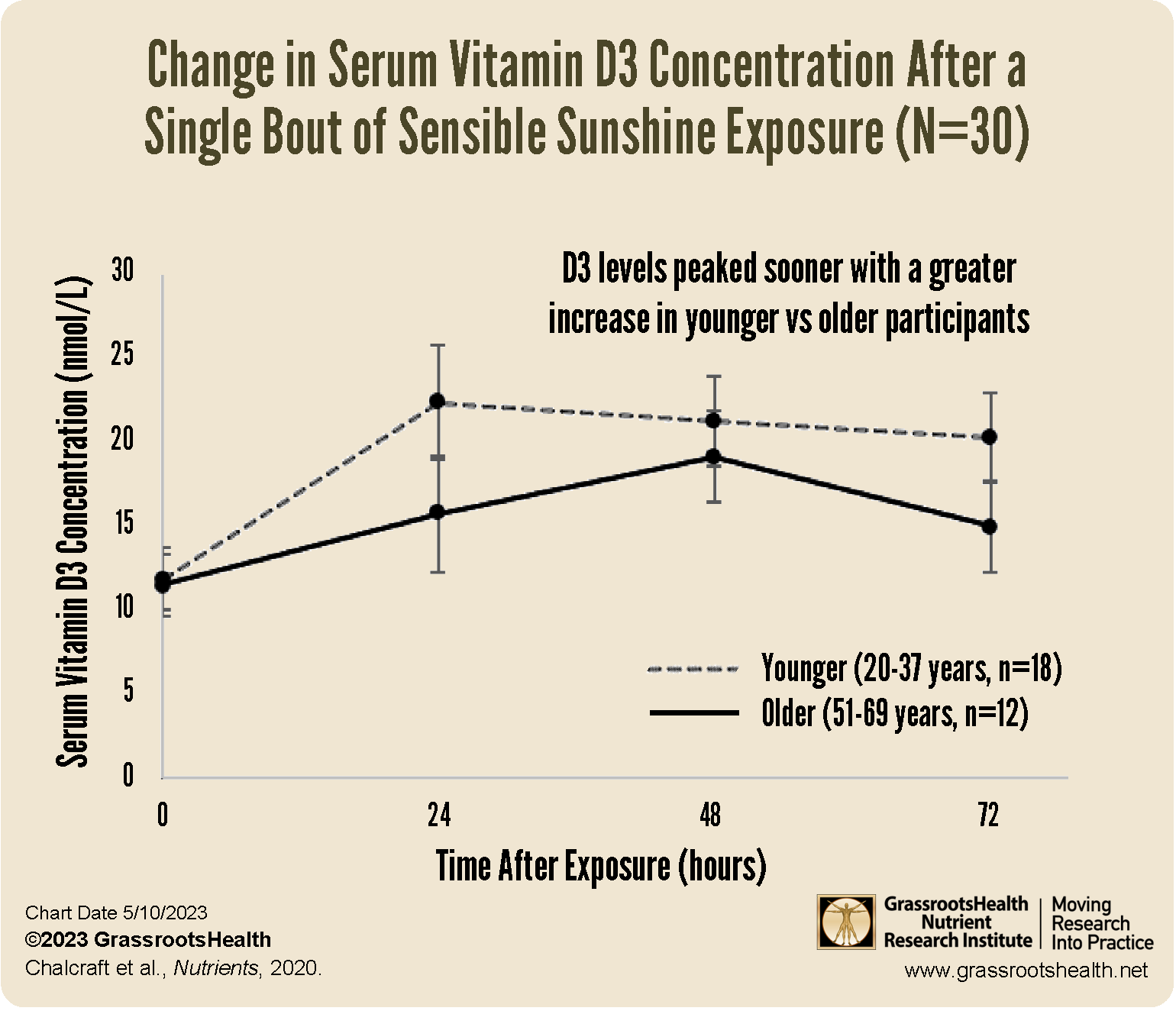
Dietary Adjustments
-
Fatty Fish: Include salmon, mackerel, and sardines in your diet.
-
Fortified Foods: Consume fortified milk, yogurt, and cereals.
-
Mushrooms: Some mushrooms are treated with UV light to increase their vitamin D content.

Physical Activity
Regular exercise can help maintain muscle strength and bone density, which are also supported by adequate vitamin D levels.

Conclusion
Vitamin D is a vital nutrient that plays a significant role in maintaining overall health, particularly for middle-aged individuals. By understanding its effects, incorporating lifestyle changes, and supplementing safely, you can ensure you’re getting enough vitamin D to support your well-being. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements to ensure they align with your specific health needs.

Additional Tips for Middle-Aged Individuals
-
Consult a Healthcare Provider: Before starting any supplements, discuss your vitamin D levels and health status with a healthcare provider.
-
Monitor Your Levels: Regularly check your vitamin D levels to adjust your supplementation as needed.
-
Combine with Calcium: If you’re taking vitamin D for bone health, consider combining it with calcium supplements.
By following these guidelines and maintaining a balanced lifestyle, you can optimize your vitamin D intake and support your overall health as you age.

Frequently Asked Questions
-
Q: How much vitamin D should I take daily?
-
A: Generally, 600-800 IU per day is recommended for adults aged 40-55. However, this may vary based on individual factors such as sun exposure and baseline vitamin D levels.
-
-
Q: What are the best food sources of vitamin D?
-
A: Fatty fish like salmon and sardines, fortified dairy products, and mushrooms treated with UV light are good sources.
-
-
Q: Can I get too much vitamin D?
-
A: Yes, taking more than 4,000 IU per day can lead to toxicity. Always consult with a healthcare provider before exceeding this amount.
-
-
Q: How often should I check my vitamin D levels?
-
A: It’s advisable to check your levels annually or as recommended by your healthcare provider, especially if you’re supplementing.
-

References
– .1 A Personalized Approach to Vitamin D Supplementation in Cardiovascular Health Beyond the Bone: An Expert Consensus by the Italian National Institute for Cardiovascular Research.
– .2 The Role of Vitamin D in the Aging Adult.
– .3 What to Know About Vitamin D Dosage for Older Adults – WebMD.
– .4 Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D response to vitamin D supplementation using different lipid delivery systems in middle-aged and older adults: a randomised controlled trial.
– .5 Calcium/Vitamin D Requirements, Recommended Foods.
– .6 Vitamin D recommendations | International Osteoporosis Foundation.
– .7 Vitamin D – Health Professional Fact Sheet.
– .8 Vitamin D: How Much to Take Per Day and Max Dose – GoodRx.
– .9 7 Nutritious Foods That Are High in Vitamin D – Healthline.
– .10 Mayo Clinic Q and A: How much vitamin D do I need?
– .11 7 Effective Ways to Increase Your Vitamin D Levels – Healthline.
– .12 Vitamin D – The Nutrition Source.
– .13 Vitamin D – Health – Canada.ca.
– .14 Effects of vitamin D supplementation on muscle strength in middle-aged and older adults.








