The Importance of Sleep for Overall Health

The Importance of Sleep for Overall Health
As we navigate the complexities of middle age, maintaining overall health becomes increasingly important. Among the various factors contributing to well-being, sleep often takes center stage due to its profound impact on both physical and mental health. For individuals aged 40-55, understanding the role of sleep in health is crucial, as this stage of life often brings new challenges and responsibilities. In this article, we will explore the significance of sleep for overall health, discuss common sleep disorders affecting middle-aged individuals, and provide practical tips for improving sleep quality.
Why Sleep Matters
Sleep is not just a passive activity; it is an essential component of our daily lives, playing a critical role in physical restoration, mental rejuvenation, and cognitive function. During sleep, the body repairs and regenerates damaged cells, builds bone and muscle, and strengthens the immune system. Additionally, sleep helps to clear waste from the brain, which may reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s .2 .12.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-the-symptoms-of-sleep-deprivation-3015161_color4-5b42c4ddc9e77c00374089b8.png)
Cognitive Health and Brain Aging
Research has shown that poor sleep quality in middle age can lead to accelerated brain aging. Studies suggest that individuals with poor sleep may have a brain age several years older than those who consistently get quality sleep .2 .7. This association highlights the importance of addressing sleep issues early in life to preserve cognitive health and potentially reduce the risk of dementia .7.
Physical Health
Sleep impacts various aspects of physical health, including cardiovascular health, weight management, and inflammation levels. Chronic sleep deprivation is linked to higher risks of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease .11. Furthermore, sleep disturbances can exacerbate conditions like hypertension and increase the risk of early mortality .11.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-the-symptoms-of-sleep-deprivation-3015161_color4-5b42c4ddc9e77c00374089b8.png)
Common Sleep Disorders in Middle Age
Middle-aged individuals are more likely to experience sleep disorders, which can significantly affect their quality of life. Some common sleep disorders include:
-
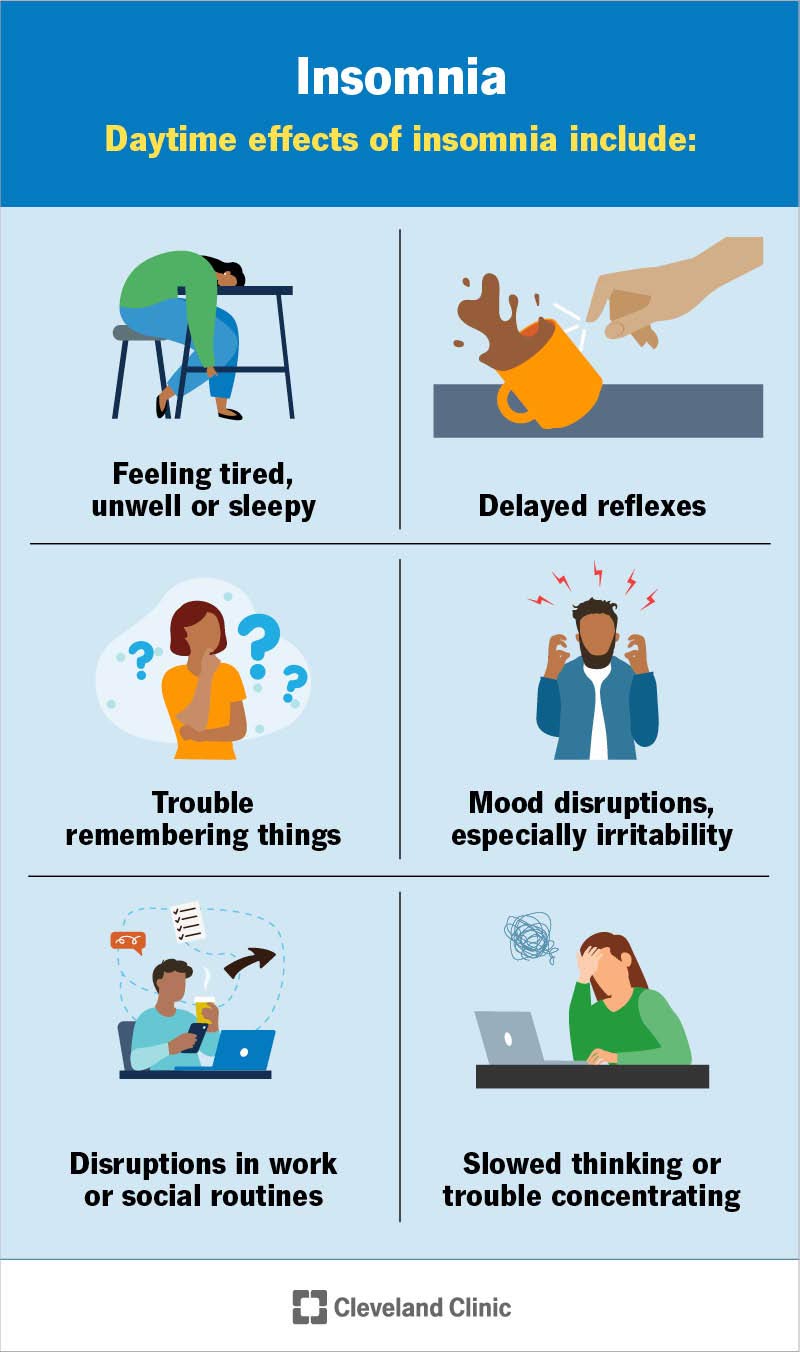
Insomnia: Characterized by difficulty falling or staying asleep, insomnia is prevalent among middle-aged adults, affecting approximately 10-15% of this population .3 .5.
-
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): OSA involves pauses in breathing during sleep and is more common in men than women. It affects about 24% of women and 47% of men in this age group .3 .5.
-
Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS): RLS causes an uncontrollable urge to move the legs, often due to uncomfortable sensations. It affects a smaller percentage of the population but can still significantly disrupt sleep .3 .5.

Improving Sleep Quality
Improving sleep quality requires a combination of lifestyle changes and consistent habits. Here are some practical tips tailored for middle-aged individuals:

1. Establish a Consistent Sleep Schedule
-
Routine: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, including weekends.
-
Timing: Aim for 7 hours of sleep, as research suggests this is ideal for cognitive function and overall health .12.

2. Create a Sleep-Conducive Environment
-
Darkness: Ensure the bedroom is dark to promote melatonin production.
-
Coolness: Maintain a cool temperature, as a cooler environment can improve sleep quality.
-
Quiet: Minimize noise with earplugs or white noise machines if necessary.
3. Limit Exposure to Electronic Devices Before Bed
-
Blue Light: Avoid screens for at least an hour before bedtime, as blue light can suppress melatonin production.
-
Relaxation Techniques: Use this time for relaxation techniques like reading or meditation.

4. Engage in Regular Physical Activity
-
Moderate Exercise: Incorporate moderate-intensity exercise into your daily routine, as it can improve sleep quality without disrupting it .6 .8.
-
Timing: Avoid vigorous exercise within a few hours of bedtime, as it can interfere with sleep onset.

5. Manage Stress and Anxiety
-
Mindfulness: Practice mindfulness or yoga to reduce stress levels.
-
Journaling: Write down your thoughts before bed to clear your mind.

6. Limit Stimulants and Heavy Meals Before Bed
-
Caffeine and Nicotine: Avoid consuming these substances in the hours leading up to bedtime.
-
Diet: Eat a light dinner and avoid heavy meals close to bedtime.

Conclusion
Sleep is a vital component of overall health, influencing both physical and mental well-being. For middle-aged individuals, addressing sleep issues is crucial to prevent accelerated brain aging, manage chronic health conditions, and maintain cognitive function. By implementing consistent sleep habits and lifestyle changes, individuals can significantly improve their sleep quality and enhance their overall health.
Additional Resources for Readers:
-
National Sleep Foundation: Offers comprehensive information on sleep disorders and tips for improving sleep quality.
-
American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Provides guidelines and resources for managing sleep disorders.
-
CDC Sleep Guidelines: Offers general advice on achieving quality sleep.
Engaging with Your Audience:
Encourage readers to share their experiences with sleep disorders and how they have improved their sleep quality. This can foster a community where individuals can support and learn from each other.
Future Article Ideas:
-
The Impact of Technology on Sleep: Explore how smartphones and other devices affect sleep patterns.
-
Nutrition and Sleep: Discuss how diet influences sleep quality.
-
Mindfulness and Sleep: Examine the role of mindfulness practices in improving sleep.
By focusing on these topics, you can create a series of articles that comprehensively address the needs and concerns of your audience regarding sleep and overall health.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-the-symptoms-of-sleep-deprivation-3015161_color4-5b42c4ddc9e77c00374089b8.png)