Understanding Hormones Changes and Impact in Midlife

Understanding Hormones: Changes and Impact in Midlife
Midlife, defined as the period between ages 40 and 55, is often a time of significant hormonal changes for both men and women. These shifts can profoundly impact physical health, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life. This article explores the hormonal changes that occur during midlife, their effects, and practical strategies to manage them effectively.
Hormonal Changes in Women
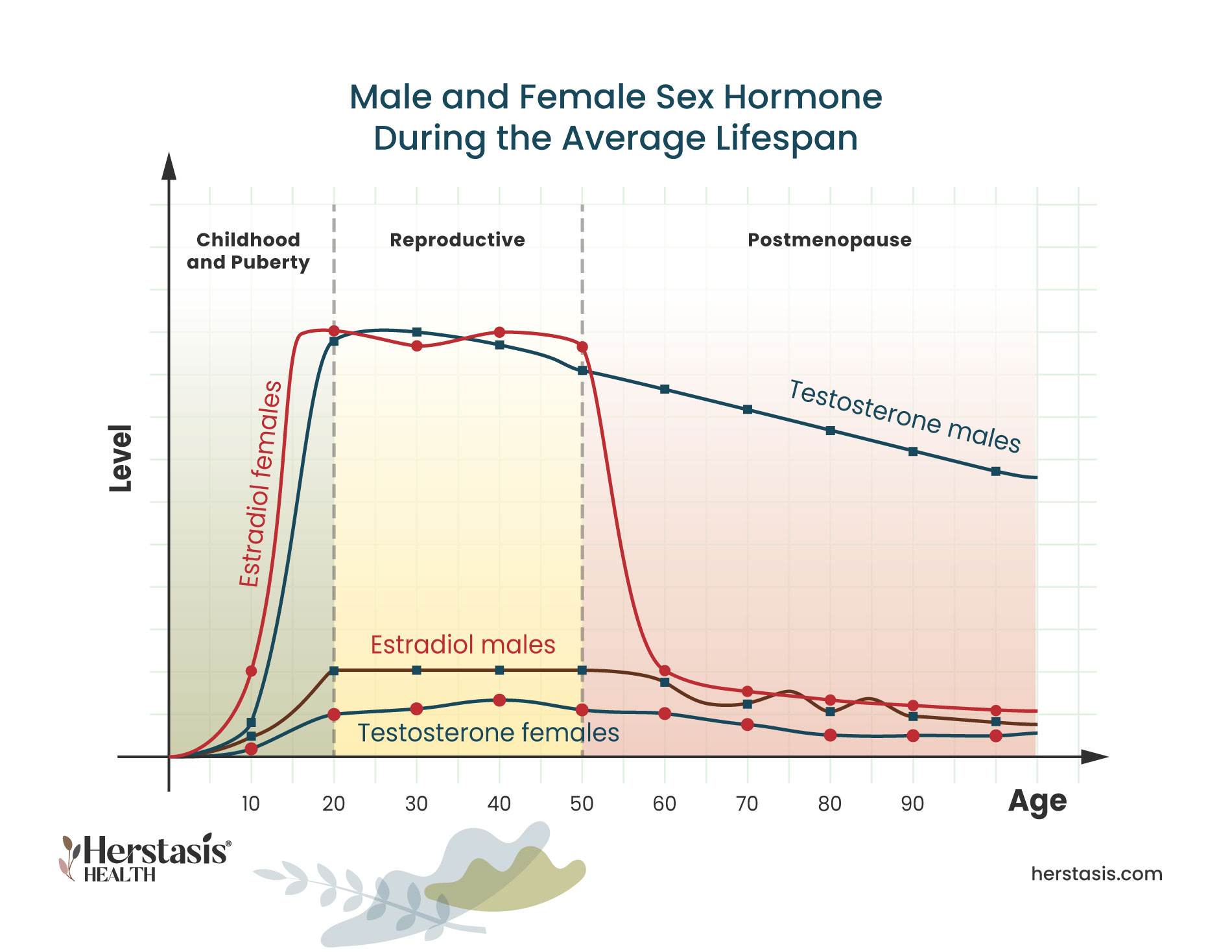
Women experience notable hormonal fluctuations during midlife due to the onset of perimenopause and menopause. These phases mark the decline in estrogen and progesterone production by the ovaries, leading to various symptoms and physiological changes.

Perimenopause
Perimenopause typically begins in a woman’s 40s and is characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, and sleep disturbances. Estrogen levels fluctuate during this phase, often causing an imbalance with progesterone levels. Stress can exacerbate these symptoms by increasing cortisol production, further disrupting hormonal balance .4 .6.

Menopause
Menopause officially begins when a woman has not experienced a menstrual cycle for 12 consecutive months. This transition usually occurs around age 50 and signifies the end of reproductive capability. The drop in estrogen levels during menopause can lead to:
-
Vaginal dryness and painful intercourse
-
Decreased libido
-
Osteoporosis due to reduced bone density
-
Weight gain, particularly around the abdomen

Impact on Physical Appearance
Hormonal changes also affect physical appearance. Skin becomes thinner and drier, hair may become brittle or gray, and fat distribution shifts towards the abdomen. These changes increase the risk of cardiovascular disease .4 .11.

Hormonal Changes in Men
While less dramatic than menopause, men experience hormonal shifts during midlife known as andropause. This phase involves a gradual decline in testosterone levels, which can lead to:
Testosterone plays a crucial role in maintaining energy levels, bone density, and overall vitality. Its decline may also contribute to cognitive challenges such as slower processing speeds or reduced problem-solving abilities .10.
Common Symptoms of Hormonal Imbalance
Both men and women may experience overlapping symptoms caused by hormonal changes during midlife:
-
Fatigue: Persistent tiredness despite adequate rest.
-
Sleep disturbances: Difficulty falling or staying asleep.
-
Mood swings: Irritability, anxiety, or depression.
-
Weight gain: Particularly around the abdomen due to metabolic slowdowns.
-
Cognitive decline: Memory lapses or difficulty concentrating .4 .8 .11.

Practical Strategies for Managing Hormonal Changes
Managing hormonal changes effectively requires a combination of lifestyle adjustments, medical interventions (if necessary), and emotional support.

Dietary Adjustments
A balanced diet can stabilize hormones and alleviate symptoms:
-
Incorporate phytoestrogens (e.g., soy products, flaxseeds) to mimic estrogen naturally .6.
-
Prioritize whole foods like leafy greens, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and lean proteins.
-
Boost calcium and vitamin D intake to support bone health.
-
Include anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric and omega-3-rich sources (e.g., walnuts) .6 .9.

Regular Exercise
Physical activity helps regulate hormones while improving mood and metabolism:
-
Strength training preserves muscle mass and supports bone density.
-
Cardio exercises like walking or swimming enhance cardiovascular health.
-
Yoga or tai chi reduce stress and improve flexibility .1 .6 .9.

Stress Management
Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, which can disrupt other hormones:
-
Practice mindfulness meditation or deep breathing exercises.
-
Engage in hobbies or journaling for emotional release.

Sleep Hygiene
Establishing good sleep habits is essential:
-
Maintain a consistent sleep schedule.
-
Avoid screens or caffeine close to bedtime.
-
Create a calming bedtime routine with herbal teas like chamomile .6 .9.

Medical Interventions
For severe symptoms:
-
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be an option but should be used cautiously due to potential risks like cardiovascular disease or breast cancer .2.
-
Non-hormonal medications can address specific symptoms like hot flashes or insomnia.
-
Regular health check-ups are essential for monitoring hormone levels .








