Understanding Liver Enzymes Important Indicators to Monitor

Understanding Liver Enzymes: Important Indicators to Monitor
Liver enzymes are crucial biomarkers that provide insight into liver health. For middle-aged individuals aged 40-55, understanding these enzymes can help identify potential health issues early and guide proactive steps to maintain liver function. This article explores what liver enzymes are, their significance, and how lifestyle choices impact their levels.

What Are Liver Enzymes?
Liver enzymes are proteins that facilitate chemical reactions in the liver. Commonly measured enzymes include:
-
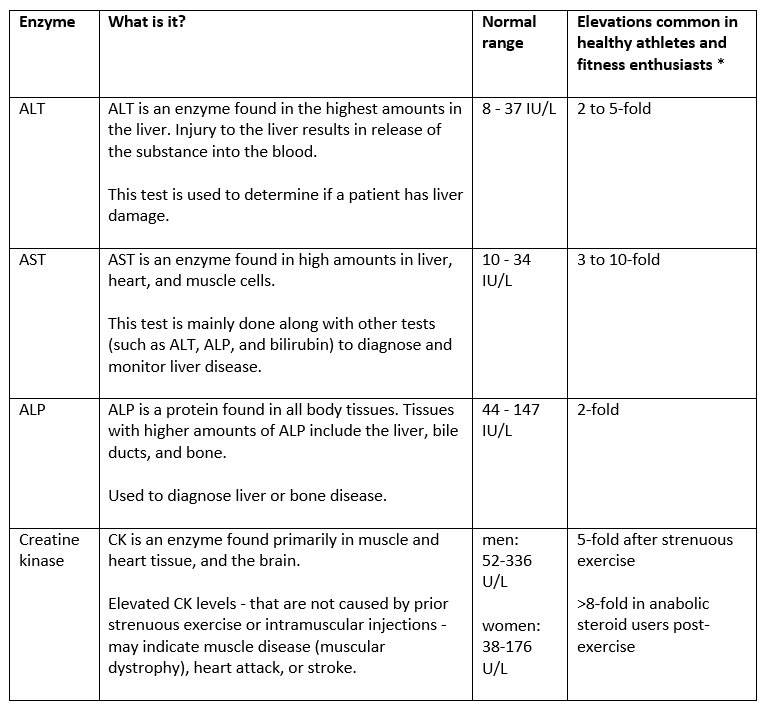
Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT): Found primarily in the liver, elevated ALT levels often indicate liver cell damage or inflammation .4 .5.
-
Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST): Present in the liver, heart, and muscles, AST levels can rise due to liver or muscle damage .4 .8.
-
Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP): Found in the liver and bones, elevated ALP levels may signal bile duct blockages or bone disorders .4 .5.
-
Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase (GGT): An enzyme linked to bile ducts, high GGT levels often indicate alcohol-related liver damage or bile duct issues .4 .5.
These enzymes are measured through blood tests to assess liver function and detect abnormalities.
Why Are Liver Enzymes Important?
Liver enzymes serve as early warning signs for various conditions:
-
Liver Diseases: Elevated enzyme levels can indicate conditions such as fatty liver disease, hepatitis, cirrhosis, or liver cancer .3 .4.
-
Metabolic Disorders: Abnormal levels may signal metabolic syndrome or diabetes .6.
-
Lifestyle Impacts: Factors like alcohol consumption, obesity, and smoking can influence enzyme levels, reflecting broader health risks .6 .14.
-
Medication Effects: Certain drugs can elevate enzyme levels, indicating potential liver stress .11.

Normal vs. Abnormal Liver Enzyme Levels
Understanding normal ranges helps interpret test results:
| Enzyme | Normal Range (U/L) | Elevated Levels May Indicate |
|---|---|---|
| ALT | 4–44 | Liver inflammation or damage |
| AST | 0–40 | Liver or muscle damage |
| ALP | 30–120 | Bile duct blockages or bone disorders |
| GGT | 0–50 | Alcohol-related damage or bile duct inflammation |
Persistently high enzyme levels warrant further testing to identify underlying causes .4 .5.

Factors Influencing Liver Enzyme Levels
Several factors can affect liver enzyme levels:
1. Age and Gender
-
Liver enzyme levels tend to increase with age in men and women. For example, ALT and AST levels are generally higher in middle-aged individuals compared to younger adults .2 .14.
-
Gender differences also exist; men often show higher ALT and AST levels than women due to lifestyle factors like alcohol consumption and body fat distribution .2 .14.

2. Lifestyle Choices
-
Alcohol Consumption: Excessive drinking is a major cause of elevated GGT and ALT levels .6 .14.
-
Obesity: Higher BMI and waist circumference are strongly linked to increased ALT and GGT levels due to fatty liver disease risk .2 .6.
-
Smoking: Smoking is associated with elevated GGT levels, especially in men .







